The septum layer is removed from the uterus surgically during septum resection, where the septum is the layer of tissue that forms during the formation of the foetus in the mother's womb. Hysteroscopic Septal Resection is whether the operation raises the possibility of a normal birth among women with a septate uterus or if the advantages exceed the risks.
Hysteroscopy is known as a procedure that is used to identify and treat uterine or womb issues. A narrow, telescope-like camera is placed through into uterus via the vaginal canal. The camera is referred to as a hysteroscope since illumination is on end.
The only technique to remove the uterus prior was to make an incision, mostly in the abdomen. However, thanks to advancements in technology, hysterectomies can now be performed without the need for an abdominal incision.
The uterus is removed surgically through the vaginal canal using this novel procedure.

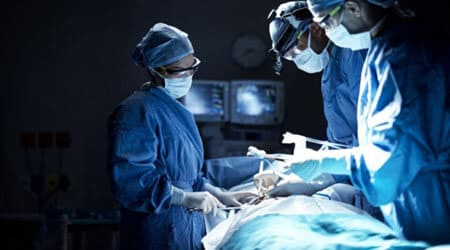
Diagnostic: It is also performed for various other reasons, such as detecting the cause of repeated miscarriages pelvic pain and finding the fertility issues apart from diagnosing the cause of abnormal bleeding.
Operative: It can be done for various purposes, such as finding and eliminating an intrauterine device implanted in the uterus for birth control, for removal of growths, for obtaining a biopsy of the tissue, and for removing the adhesions.
Laparoscopic hysterectomies meant a quicker return to normal activities, less blood loss and a smaller drop in blood count, a shorter stay in the hospital, and fewer wound infections and episodes of raised temperature after surgery than abdominal hysterectomies. But laparoscopic hysterectomies have a greater risk of damaging the bladder or ureter (the tube leading to the bladder from the kidney) and are longer operations.
To help the patient relax and relieve the pain during the procedure, they are given sedatives. Also, medicine may be inserted to open the cervix.

Complications or side effects are likely to occur in patients having operative hysteroscopy instead of diagnostic hysteroscopy.

With the discovery of the vaginal path for hysterectomy for non-descent uteri, gynaecologists discovered a means to perform hysterectomy without leaving a scar on the abdomen, known as scarless hysterectomy.
This procedure includes several advantages such as Economically feasible, No formation of scar, and is useful for patients who have benign diseases priorly.

Are you an international patient looking for the best gynecological care in India? Consult Dr. Sarada Mamilla, the best gynecologist & Laparoscopic Surgeon in India, offering top notch care for complex cases of uterine fibroids, endometriosis, adenomyosis & gynecological malignancies.
Copyright © 2023 All rights reserved By Dr.Sarada